By: Per Friis Knudsen & Emma Wallace
Humans have utilised wood since we first had a tool in our hands. Today, we walk on wooden floors, open wooden doors, sit in wooden furniture, walk on wooden stairs, we build houses in wood, have wooden panels here and there. Everywhere you look, you’ll almost certainly see something made of wood. But wood has many other possibilities and new inventions are constantly popping up. We have done a little to research on the topic and found some interesting items that we’d like to share with you.
Cellulose walls and nanofibers
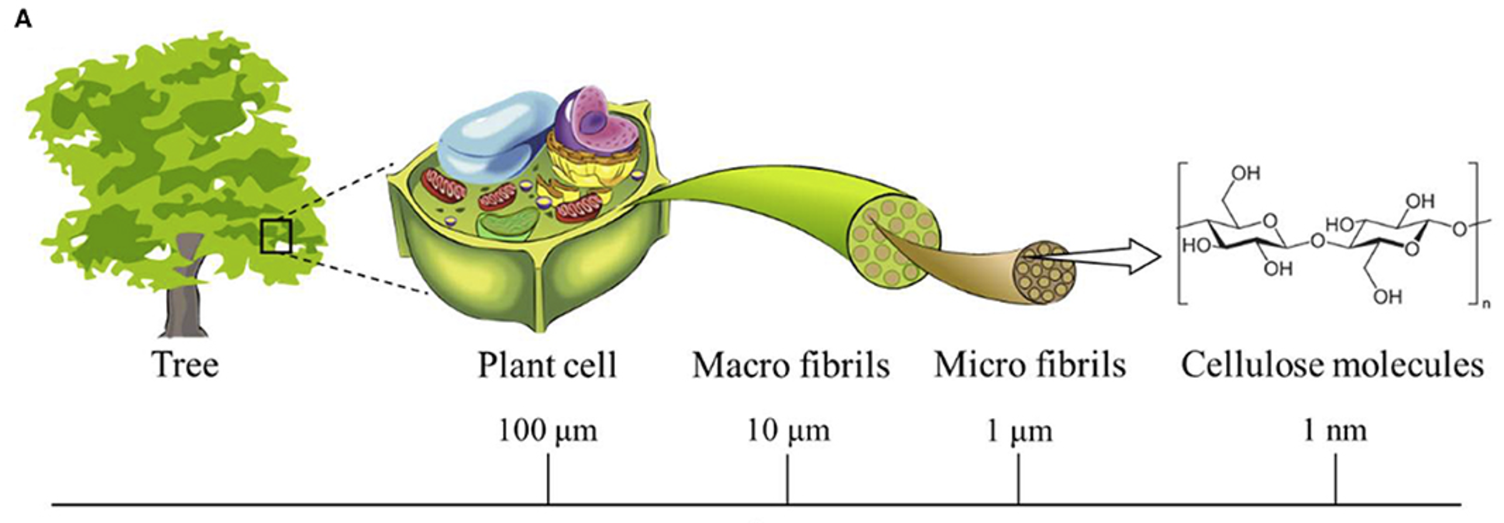
As this article is a part of our theme on wood science, we will start out with a little necessary scientific explanation. Many of the new inventions made from wood consists of cellulose or nanofibers. These are extracts from the timber itself and the extraction process can be both difficult and expensive. Cellulose in wood is an important structural component of the cell wall in green plants and to draw a parallel, imagine it as reinforcing steel bars when building wall in a house.
Nanocellulose is then a term referring to tiny little cellulose fibres from these plant walls. To learn how to extract such things is a study in itself and I believe there are fortunes to be made in inventions to help the world become greener. The deepest respect goes out to any scientists who is working in this area, and we applaud those who have succeeded with this process. Hopefully, it will be an everyday thing in the future.
An equally important part of the utilisation process of wood is lignin. Lignin is roughly said the “concrete” of the wooden cell walls. So, to use our metaphor of the building of a house from before, the lignin is the “concrete” that covers the cellulose “reinforcing steel bars” and thereby, they make up a solid cell wall for the plant. Wood and bark would not be what it is without lignin; especially as lignin is what keeps the plants from decomposing and it makes up about a third of woods composition.
Now, let’s look at some examples of what wood can be used for.
3D Printing
One of the first examples is within the world of 3D printing. Apparently, the material that is used for 3D printing can be mixed with nanoparticles from wood, which improves its properties to build 3D structures. Traces of lignin and nano-fibrillated cellulose can reduce the temperature of the material used for printing and this gives better properties in the bending and stretching abilities. Scientists at the Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden succeeded to simulating wooden ultrastructure in 3D-ink. Imagine what possibilities this would bring to many new inventions – printing clothing, packaging, or furniture with unique green properties by using the natural cellular architecture of wood. It should make the need for plastic packaging decrease as well.
Battery and energy storage
This example is a little more technical. The Finnish company, Stora Enso, has built a €10 million production facility that will create renewable bio-based carbon by turning trees into batteries. Again, lignin is the key material for this production. Similarly, Ligna Energy from Sweden is also working on this, so the chances are good for this invention. The goal is “to have a cost efficient, safe, and environmentally friendly solution for energy storage that promotes a global accelerated shift towards fossil-free energy production“. At the moment, the energy can be used in car charging stations. If all goes well, the batteries might be able to one day replace lithium-ion batteries that we know from vehicles. Imagine all the batteries we use in everything from electric and hybrid cars to electric-powered bicycles and scooters. And to top it all off, the batteries are biodegradable in the sense that when they can be recycled or burnt as biofuel. In this article, there is a very interesting video from one of the companies that explain a lot more about this exciting innovation.
Oil-absorbing material and clean water
We are all dependent on oil in our everyday use of electronics, heating, and so much more. But oil has long created a risk for the world’s oceans as oil spills have a heavy impact on sea- and wildlife. It might not happen often, but when it does, it has huge consequences. Birds become covered in oil and their feathers cannot become clean enough to fly again. Residue from the oil spreads into the ocean and particles are eaten by fish. Previously, oil spills have been the cause for some very serious damage to the environment as the clean-up possibilities has been very limited. Now there might be a solution in sight. Based on cellulose from wooden fibres, a company called Biosorber has made an absorbing material that contains oil-eating microbes and turning them into harmless substances. The material separates the oil and the water, so even the material is removed, it takes the oil with it and leaves clean filtered water. They have made a great video to illustrate the idea of the concept.
Transparent wood
Lastly, our favourite example. In 2016, Per was very excited to read about new inventions with transparent wood by researchers from the University of Maryland. The scientific part once again revolves around lignin, but this time the material is cooked or boiled, so a fairly transparent resin is left. The material is not totally transparent and clear as we would imagine a normal windows, but this material would fit perfectly as a window for a bathroom with a frosted look. Back then, it was only possible to make a 10cm x 10cm transparent surface and the process involved epoxy, which isn’t exactly environmentally friendly. But it had some great qualities – it was stronger than normal glass, good for insulation purposes and most importantly, it was biodegradable. There can be envisioned many great uses for this invention in the future, so there are strong hopes to see this succeed into bigger and better things.

These inventions might not have seen the light of day yet, but we have faith in the many possibilities and uses of wood in untraditional ways. Many inventions that we use today would have seemed impossible just 10 years ago. But that’s why it is so important to keep searching for new solutions and keep innovating. It will take us further than we can imagine – but only if we keep trying. For one, we will continue to dream about new wooden inventions; maybe one day we will have wooden degradable solar cells or something completely new.